

Each of these items has the potential to harbor pathogens and transmit disease if not properly sanitized between patient. Countless pieces of equipment and supplies come into contact with spay‐neuter patients throughout their clinic experience. In the human medical field, surgical site infections (SSIs) occur in 3% of all surgical procedures and make up 14‐22% of all healthcare‐associated infections. Maintaining asepsis is considered the standard of care for surgical sterilization and has a direct impact on patient outcome. In the future, immunohistological staining and gene sequencing may also facilitate the development of individualized therapies for those with disseminated disease at the time of diagnosis. Using anatomic sequences, diagnostic radiologists can assist their surgical and radiation oncology colleagues in defining tumor boundaries, assessing the involvement of adjacent structures, and ultimately determining the feasibility of en bloc resection. Additionally, thorough radiographic evaluation with magnetic resonance imaging, high-resolution computed tomography, and nuclear medicine or other staging scans enhances treatment planning. The conjunction of radiographic and histologic features allows for the differentiation of benign and malignant notochordal neoplasms from one another and from other entities in the differential. Hence, the image-guided biopsy is necessary for definitive diagnosis.

Similarities in the imaging characteristic of these lesions may lead them to occasionally be completed with other neoplastic or infectious processes. This family includes both benign notochordal cell tumors (BNCTs), e.g., giant vertebral notochordal rest tumors, eccordosis physaliphora, and the various subtypes of chordoma (classic, chondroid, and undifferentiated).
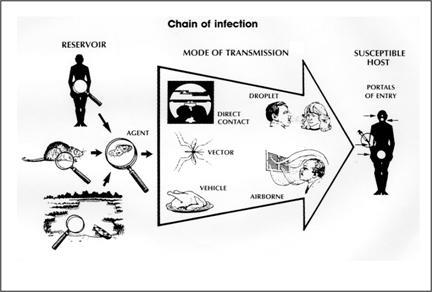
#DEFINITION OF MEDICAL ASEPSIS SKIN#
Therefore, it is recommended to use a single blade for skin incision and a new blade for the remaining surgical approach, reducing the potential of bacteria dissemination into deeper tissues by the first skin incision bladeĬhordomas are rare malignancies belonging to a family of lesions derived from the primitive notochord. Although no dog has developed SSI, the present report showed that the scalpel blade may act as a dissemination vehicle of potential bacterial pathogens to superficial or internal tissues of dogs undergoing surgery, potentially leading to SSI development. Nevertheless, all samples were negative for methicillin-resistant bacteria. However, only 10.8% (5/46) of the positive blade samples also corresponded to a positive post-asepsis sample. Results showed that 30.4% (14/46) and 28.3% (13/46) of the post-asepsis and blade samples originated positive bacterial cultures in BHI agar, respectively. From each animal two swab samples were collected, from the skin post-asepsis and from the scalpel blade after skin incision, for bacterial growth evaluation in Brain Heart Infusion (BHI) agar and detection of methicillin-resistant species. A total of 46 dogs presented for orthopedic or soft tissue surgery in different anatomical regions were included in this study. Due to their importance in veterinary medicine, the role of surgical blades in bacterial dissemination to internal tissues of dogs undergoing surgery was evaluated. Surgical site infections (SSI) are post-surgical incisional infections in superficial or deep tissues, including organs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
